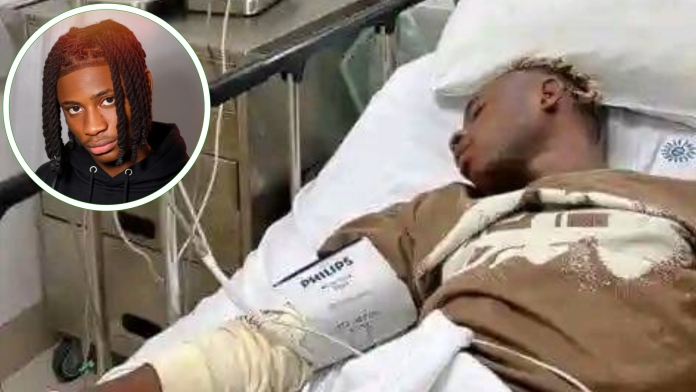
- Khaid is hospitalized and suffering from severe internal bleeding illness.
- Khaid’s music career began under Neville Records, introduced by Sydney Talker.
- Fans and the music industry are hoping for Khaid’s swift recovery.
Khaid, a promising talent in the Nigerian music scene and a signee under the management of comedian and influencer Sydney Talker, has been hospitalized due to complications from internal bleeding. This condition has caused significant concern among fans, industry insiders, and fellow artists. The sudden hospitalization has left many shocked and deeply concerned for his well-being.
Internal bleeding is a serious condition where blood leaks into the tissues or cavities of the body, leading to complications such as organ damage, infection, and potentially life-threatening conditions. The specifics of Khaid’s internal bleeding condition, including the cause and the extent of the damage, have not been disclosed by Sydney Talker or his management team. This lack of transparency has sparked calls for updates and reassurance regarding Khaid’s health and recovery process.
The situation has prompted a heartfelt plea in a video from Carter Efe, a fellow musician, who urged Sydney Talker to clarify Khaid’s health status. Efe’s emotional outcry underscores the growing anxiety among fans and industry insiders alike, who are eager to know the full extent of Khaid’s illness. The distressing news has also led to a pressing need for transparency and open communication from Sydney Talker and his management team.
Before the call out, Sydney Talker took to his Instagram page to call for prayers and support for his signee. He has emphasized the importance of collective prayers, urging his followers to pray for Khaid’s recovery.
Causes of Internal Bleeding
Internal bleeding, a condition where blood leaks into the tissues or cavities of the body, can be caused by a variety of factors[1]. The causes of internal bleeding are as varied as the symptoms and can range from external trauma to internal conditions or drug overuse. Trauma is one of the most common causes of internal bleeding. It can be categorized into two main types:
- Blunt trauma occurs when a body part collides with something else at high speed, causing blood vessels inside the body to be torn or crushed. Examples include car accidents, physical assaults, and falls.
- Penetrating trauma happens when a foreign object penetrates the body, tearing a hole in one or more blood vessels. This can result from gunshot wounds, stabbings, or falling onto a sharp object.
These types of trauma can damage almost any organ or blood vessel, leading to internal bleeding. Serious sources of internal bleeding due to trauma include head trauma (intracranial hemorrhage), bleeding around the lungs (hemothorax), bleeding around the heart (hemopericardium and cardiac tamponade), tears in large blood vessels near the center of the body (aorta, superior and inferior vena cava, and their major branches), and damage to the abdomen, such as liver or spleen lacerations or perforation of other organs.
Bleeding disorders, such as hemophilia, can also lead to internal bleeding. This condition is caused when blood does not clot as it should, due to the lack of blood cells called platelets or proteins called clotting factors. The overuse of certain drugs, including blood thinners like warfarin and anti-platelet drugs like Plavix (clopidogrel), can also increase the risk of bleeding. Even nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like aspirin and Advil (ibuprofen) can cause internal bleeding if used excessively, especially in individuals with peptic ulcers or any other condition that causes gastric (stomach) bleeding.
Viral hemorrhagic fevers are a less common but potentially serious cause of internal bleeding. Certain viruses can cause small blood clots to form in blood vessels throughout the body, reducing the availability of platelets to stop bleeding. These fevers are most common in Africa and include Chikungunya fever, Dengue fever, Ebola virus, Hantavirus, Lassa fever, Rift Valley Fever, and Yellow fever.
Organ damage or a bleeding disorder can also lead to internal bleeding. Conditions like gastritis can increase the risk of bleeding, and organ damage can result in internal bleeding if the damage affects blood vessels or organs that are prone to bleeding.